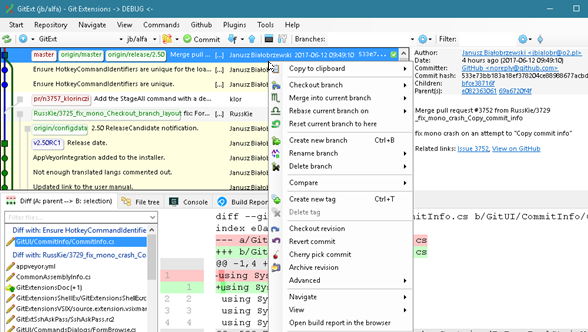
The following example uses a GitHub host, but you can use any Git host for version control in Visual Studio for Mac. To set up a Git repository, execute the following steps: Create a new Git repo at github.com: Set Repo Name, description, and privacy. Do not initialize Repo. Set.gitignore and license to None. Fork - a fast and friendly git client for Mac and Windows. About Us Blog Release Notes Home. A fast and friendly git client for Mac and Windows. Fork is getting better and better day after day and we are happy to share our results with you. Download Fork for Mac. OS X 10.11+ $49.99, free evaluation. Checkout extensions modify the git operations that place files in the workspace from the git repository on the agent. The extensions can adjust the maximum duration of the checkout operation, the use and behavior of git submodules, the location of the workspace on the disc, and more. It comes with built-in support for TypeScript, JavaScript and Node.js, has integrated Git and a wide range of extensions for other languages. By using its various settings, you can configure this software for Mac app development to your needs: almost every part of its editor, UI, and functional behavior has options you can modify.
This section is primarily written for Windows users. There are extra sectionsabout installing Git Extensions on Linux and Mac OS X.
Installation¶
There is a single click installer that installs MsysGit, Kdiff3 and Git Extensions. The installer will detectif 32bit and/or 64bit versions should be installed.The installer can be found here.
Git Extensions depends heavily on MsysGit. When MsysGit is not installed, ensure the “Install MsysGit” checkbox is checked. Kdiff3 isoptional, but is advised as a merge tool.
Choose the SSH client to use. PuTTY is the default because it has better Windows integration.
Installation (Linux)¶
You can watch this video as a starting point: Install Git Extensions on Ubuntu 11.04
For further help go to https://groups.google.com/forum/?fromgroups=#!forum/gitextensions
Installation (Mac)¶
This section only covers mono installation, you should have git installed in your Mac at this point. Please refer to http://git-scm.com/downloads
First, make sure you have the latest mono version on your Mac. This section will cover installation of mono 3.8.0 on a Mac.
Download mono latest version. You can always check for this here: http://www.go-mono.com/mono-downloads/download.html
After you have completed the download, you will see a .dmg file. Double click it to open the package.
Inside the .dmg file you will have MonoFramework-{version}.pkg. Double click to start the installation process.
Follow the wizard until it’s completion.
If everything went okay, you should open your terminal and check mono version:
Now download Git Extensions latest version from https://sourceforge.net/projects/gitextensions. Remember to select the appropriate package otherwise you could have problems.
Browse into the folder where you extracted the package and just run mono command, like the example below:
This is the minimal setup you need in order to run Git Extensions.
Troubleshooting Mac Installation¶
- If your Git Extensions crashes with an exception that a font is missing (generic sans serif), you probably can fix this by installing Xquartz. This is a version of the X.Org X Windows System that runs on OS X. I am not sure what the side effects are. This can be installed from here: http://xquartz.macosforge.org/landing/
- If Git Extensions still crashes because it is unable to load a plugin, empty the plugins folder.
Settings¶
All settings will be verified when Git Extensions is started for the first time. If Git Extensions requiresany settings to be changed, the Settings dialog will be shown. All incorrect settings will be marked in red.You can ask Git Extensions to try to fix the setting for you by clicking on it.When installing Git Extensions for the first time (and you do not have Git already installed on your system),you will normally be required to configure your username and email address.
The settings dialog can be invoked at any time by selecting Settings from the Tools menu option.
For further information see Settings.
Start Page¶
Download vegas pro free for mac. The start page contains the most common tasks, recently opened repositories and favourites. The left side of the start page (Common Actionsand Recent Repositories) is static. The right side of the page is where favourite repositories can be added, grouped under Category headings.
Recent Repositories can be moved to favourites using the repository context menu. Choose Movetocategory/Newcategory to create a new categoryand add the repository to it, or you can add the repository to an existing category (e.g. ‘Currents’ as shown below).
A context menu is available for both the category and the repositories listed underneath it.
Entries on Category context menu
| Move Up | Move the category (and any repositories under it) higher on the page. |
| Move Down | Move the category (and any repositories under it) lower on the page. |
| Remove | Remove the category (and any repositories under it) from the page. Note: Git repositories are notphysically removed either locally or remotely. |
| Edit | Shows the Start Page settings window where both category and repository details can be modified.See Start Page. |
Entries on repository context menu
| Move to category | Move the repository to a new or existing category. |
| Move up | Move the repository higher (within the category). |
| Move down | Move the repository lower (within the category). |
| Remove | Remove the repository from the category. Note: the repository is not physically removed eitherlocally or remotely. |
| Edit | Shows the Start Page settings window where both category and repository details can be modified.See Start Page. |
| Show currentbranch | Toggles the display of the branch name next to the repository name. This identifies the currentlychecked out branch for the repository. |
To open an existing repository, simply click the link to the repository under Recent Repositories or within the Categories that you have set up, orselect Open repository (from where you can select a repository to open from your local file system).
To create a new repository, one of the following options under Common Actions can be selected.

Clone repository¶
You can clone an existing repository using this option. It displays the following dialog.
The repository you want to clone could be on a network share or could be a repository that is accessed through an internetor intranet connection. Depending on the protocol (http or ssh) you might need to load a SSH key into PuTTY. You also need to specify wherethe cloned repository will be created and the initial branch that is checked out. If the cloned repository contains submodules, then thesecan be initialised using their default settings if required.
There are two different types of repositories you can create when making a clone. A personal repository contains the completehistory and also contains a working copy of the source tree. A central repository is used as a public repository wheredevelopers push the changes they want to share with others to. A central repository contains the complete history but does nothave a working directory like personal repositories.
Clone SVN repository¶
You can clone an existing SVN repository using this option, which creates a Git repository from the SVN repository you specify.For further information refer to the Pro Git book.
Clone Github repository¶
This option allows you to
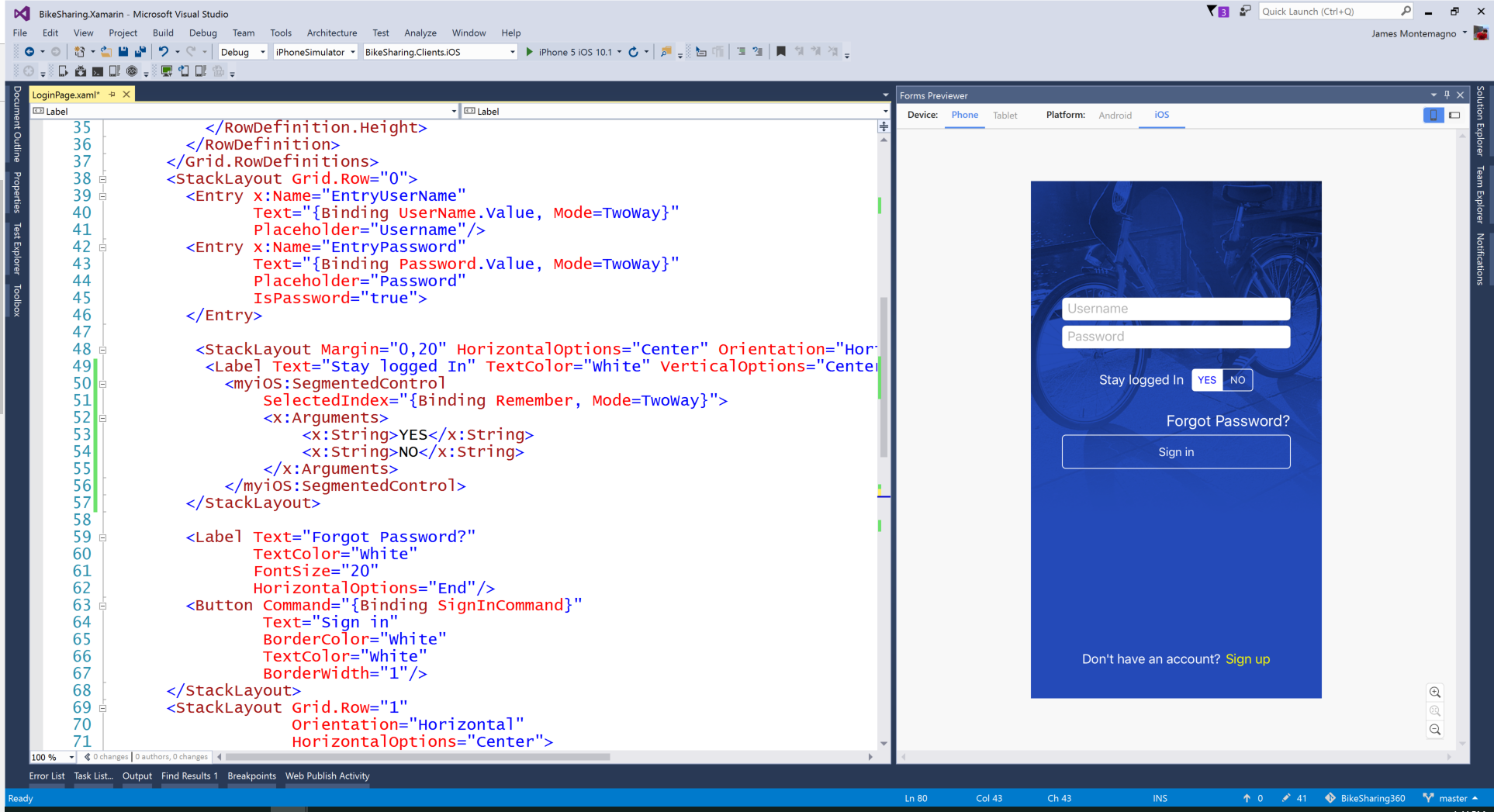
- Fork a repository on GitHub so it is created in your personal space on GitHub.
- Clone any repositories on your personal space on GitHub so that it becomes a local repository on your machine.
You can see your own personal repositories on GitHub, and also search for repositories using the Searchforrepositories tab. Archive for mac download.
Create new repository¶
When you do not want to work on an existing project, you can create your own repository using this option.
Select a directory where the repository is to be created. You can choose to create a Personal repository or a Central repository.
A personal repository looks the same as a normal working directory but has a directory named .git at the root levelcontaining the version history. This is the most common repository.
Central repositories only contain the version history. Because a central repository has no working directory you cannotcheckout a revision in a central repository. It is also impossible to merge or pull changes in a central repository. Thisrepository type can be used as a public repository where developers can push changes to or pull changes from.

Installing and configuring Git on macOS can seem difficult if you’ve never used a command line before, but there are only a few things to learn to get started. This guide will take you through the steps to install and configure Git and connect it to remote repositories to clone, push, and pull.
Installing Git
Git Plugin For Mac
Download the latest Git installer package, double click on the installer to start the installation wizard. You’ll be prompted for your system password in order for the installer to complete.
After you have successfully installed Git on Mac, you’ll need to provide secure communication with your Git repositories by creating and installing SSH keys.
Creating SSH keys on Mac
To communicate with the remote Git repository in your Beanstalk account from your Mac, you will need to generate an SSH key pair for that computer. This process requires only a few steps, and all of the tools necessary are included on your Mac.
Launching Terminal
Terminal is an application that comes with macOS and provides you with an interface to run text commands, switch through folders, and manage files. You can usually find it in your Applications → Utilities folder.
Generating a key pair
Type these commands in your Terminal window and press Return. First make sure you are in your home directory:
and then generate the keypair with:
It will ask for location, just accept the default location (~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub) by pressing Return. When it asks for a pass phrase, make sure to set a strong pass phrase for the key. We’ve included some additional information about SSH keys and how to manage strong pass phrases in our Tips for using SSH Keys guide.
Now that the keys are generated, copy it to your clipboard for the next step:
Your public key is now on your clipboard and you can easily add it to a version control hosting account like Beanstalk. When you paste it, your SSH public key should look something like this:
In your Beanstalk account, the added SSH key will look like this:
Checking your connection
Before trying to access your Git remote repository, check if the connection to your remote hosted Git repository works. Enter the following command in the Terminal, replacing “accountname” with your account name:
In this case, this is the URL to access Git on your Beanstalk account. If you are using another version control hosting service, the URL would be provided by them.
You’ll most likely encounter a message that looks like this:
You can type yes and press Enter, which will add your account’s hostname accountname.beanstalkapp.com to a known_hosts file. This step won’t need to be repeated unless your public key or your account names changes. Also, this must be done from the Terminal before using any GUI clients.
If you were authenticated correctly, you will see a message similar to this one:
You can now continue to configure your local Git profile.
Setting up your Git Profile
After you have authenticated correctly by installing Git and setting up SSH keys, before you start using your Git repositories, you should setup your Git profile by typing following after you run Git bash in command line:
In case you are using Beanstalk for version control, it would be best if your first name, last name and email address match to the ones you use in your account to avoid any conflicts.
Summary
In order to be able to use your repository you need to:
- Install Git
- Generate SSH keys with
ssh-keygen - Check if the connection to the Git repository is working
- Set up your Git profile
Git Extensions Plugins
While getting started with Git, the most common mistakes include mismatched private and public SSH keys or the Beanstalk user not having permission to access the repository. Make sure to check these after you have finished setting up Git. If you run into issues, just contact us using one of the links below.
Now what?
Git Extensions Portable
Now that you have Git properly installed and configured, you can use a client of your choice. Whether you choose a terminal or a GUI, it is a good idea to learn the basic concepts and commands for versioning your files before. Here’s some recommended reading to get you started:
- Git Immersion Tutorial – an excellent step-by-step tutorial to using Git
- Pro Git E-book and Printed Edition
- The Git Parable – understand the concepts behind Git with a simple story by Tom Preston-Werner
